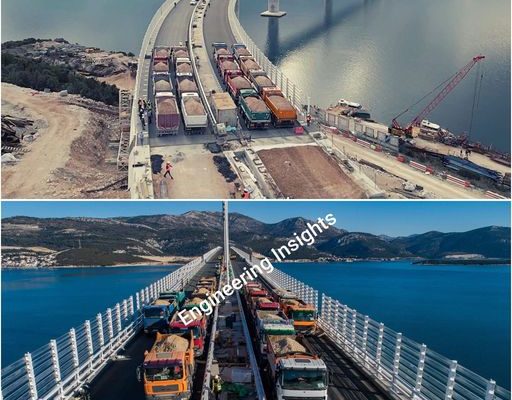
A bridge load test is a procedure used to assess the structural integrity and performance of a bridge by applying loads and measuring its response. The main objectives of a bridge load test are to verify design assumptions, determine load-carrying capacity, and identify any potential weaknesses or areas needing maintenance.
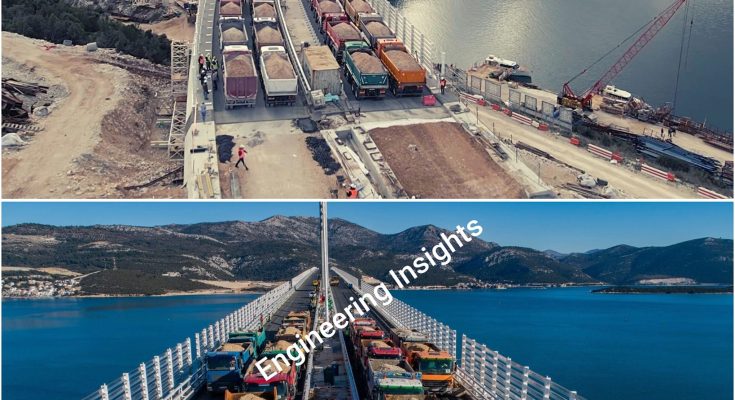

A bridge load test is a procedure used to assess the structural integrity and performance of a bridge by applying loads and measuring its response. The main objectives of a bridge load test are to verify design assumptions, determine load-carrying capacity, and identify any potential weaknesses or areas needing maintenance.
Types of Bridge Load Tests
1. Static Load Test:
– Procedure: Known loads (e.g., trucks with known weights) are placed at specific locations on the bridge.
– Measurements: Deflections, strains, and stresses are measured to compare with theoretical values.
– Purpose: To verify the bridge’s behavior under stationary loads.
2. Dynamic Load Test:
– Procedure: The bridge is subjected to moving loads or impact loads (e.g., vehicles crossing the bridge at various speeds).
– Measuremen: Vibrations, natural frequencies, damping ratios, and dynamic responses are recorded.
– Purpose: To assess the bridge’s performance under real-world dynamic conditions.
Steps Involved in a Bridge Load Test
1. Preparation:
– Review bridge design and historical data.
– Develop a detailed load test plan, including safety measures.
– Obtain necessary permits and inform relevant authorities.
2. Instrumentation:
– Install sensors and measurement devices (e.g., strain gauges, displacement transducers, accelerometers) at critical points on the bridge.
– Ensure proper calibration and functioning of all instruments.
3. Execution:
– Apply static or dynamic loads as per the test plan.
– Gradually increase the load while monitoring the bridge’s response.
– Ensure safety throughout the testing process.
4. Data Collection and Analysis:
– Record data from all sensors and measurement devices.
– Compare the measured responses with theoretical predictions and design values.
– Identify any discrepancies or unexpected behavior.
5. Reporting and Conclusions:
– Compile the data and analysis results into a comprehensive report.
– Provide recommendations for maintenance, repairs, or further testing if needed.
– Update the bridge’s load rating if necessary.
Bridge load tests are critical for ensuring the safety and longevity of bridge structures, helping engineers make informed decisions about maintenance and upgrades